Help
User Manual
User Manual of SCG-Drug: This document describes how to use SCG-Drug.
Web Server Access
The SCG-Drug web interfaces allow users to explore medical genetic information related to a given drug, disease or gene through four interfaces: Drug, Gene, Disease and Batch prediction:
The Drug interface allows users to submit a single drug or a file containing multiple drugs to explore their potential activities. For example, when a user submits a single drug that was shown in the dropdowns, it will search the database directly for this drug. If it is unable to find any matches for the search term, it will ask the user to input the corresponding target genes of the drug. Then, it will call the prediction module.
The Gene interface allows users to explore gene-related diseases and drugs only by submitting a gene name or an Entrez ID, which are included in the server. In addition, users can download overall information.
The Disease interface allows users to obtain relevant disease genes with druggability score, and database source by querying standardized disease descriptions of MeSH.
Alternatively, the system allows the user to upload a file on the Batch prediction interface, in which an agent and corresponding targets are in a single row and the terms in each row are separated by tabs, along with an email address to which the predicted activities of the agents will be sent. Offline prediction automatically starts, and the predicted results are sent to the user via e-mail.
FAQ
What is the goal of SCG-Drug?
To help you to predict potential activities of drugs of interest with respect to their genetic information.
What types of drug names/symbols should I use as input?
Any drug names. But there are total 5,759 drugs included in SCG-Drug database. The drug names are listed in the drugs.txt. Therefore, when you submit a drug name that was listed in the text, SCG-Drug will search the database directly for this drug. If it is unable to find any matches for the search term, it will ask you to input the corresponding target genes of the drug. Then, it will call the prediction module.
What types of gene names/symbols should I use as input?
When you want to get the related information of genes at Gene interface, you could type in HGNC gene symbols or Gene Entrez ID.
But when you want to predict a drug's potential activities at Drug interface, you should only type in HGNC gene symbols. Or you will get incorrect results!
What types of diseases should I use as input?
The “Disease” interface allows users to obtain relevant disease genes with druggability score, and database source by querying standardized disease descriptions of MeSH.
What kind of supported format file should I upload?
The upload file is a TAB delimited file without comment line or header. The first column is a drug name, the following columns are gene symbols:
drug1 IL12A IL10 SLC6A4 CTLA4 drug2 AGGF1 BRK1
What is druggability score of disease gene?
We proposed a parameter named druggability score for quantitatively measuring the druggability of disease genes. First, the genes derived from different databases were given different scores, with the highest-quality database (i.e., Clinvar) being assigned with the highest score (eight points), while the lowest (i.e., DisGeNET) with the lowest score (one point). Then, the scores were summed up for each disease gene to define its druggability:
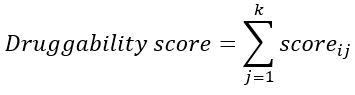
where scoreij denotes the assigned score of a pathogenic gene i in the jth database ; i = 1, 2, ..., m; j = 1, 2, ..., k, where m is the number of disease genes, k is the number of databases (k = 8 in this study).
What are the abbreviations used at SCG-Drug?
Ref. = reference. | Wang, X., et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of protein networks provides insight into human genetic disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 159–164 (2012)
GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Studies.
GAD = Genetic Association Database. | The Genetic Association Database is a database of genetic association data from complex diseases and disorders.
OMIM = Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. | OMIM is a comprehensive, authoritative compendium of human genes and genetic phenotypes that is freely available and updated daily.
ClinVar = ClinVar. | ClinVar is a freely accessible, public archive of reports of the relationships among human variations and phenotypes, with supporting evidence.
Orphanet = Orphanet. | Orphanet is the reference portal for information on rare diseases and orphan drugs, for all audiences.
GWASdb = GWASdb. | GWASdb is a one stop shop which combines collections of traits/diseases associated SNP (TASs) from current GWAS and their comprehensive functional annotations, as well as disease classifications.
NHGRI GWAS Catalog = NHGRI GWAS Catalog. | The Catalog is a quality controlled, manually curated, literature-derived collection of all published genome-wide association studies assaying at least 100,000 SNPs and all SNP-trait associations with p-values < 1.0 x 10-5 (Hindorff et al., 2009).
RegulomeDB = RegulomeDB. | RegulomeDB is a database that annotates SNPs with known and predicted regulatory elements in the intergenic regions of the H. sapiens genome.
HGMD = The Human Gene Mutation Database. | The HGMD represents an attempt to collate known (published) gene lesions responsible for human inherited disease.
DGIdb = Drug-Gene Interaction database. | Drug-Gene Interaction database.
TTD = Therapeutic Target Database. | TTD is a database to provide information about the known and explored therapeutic protein and nucleic acid targets, the targeted disease, pathway information and the corresponding drugs directed at each of these targets.
DrugBank = DrugBank. | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug target information.
ClinicalTrials = ClinicalTrials.| ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world.
 loading..
loading..